Table of Contents
ToggleDiscovering iganonu might just be the game-changer you’ve been waiting for. This powerful traditional remedy has been used for centuries in West African communities, yet it’s only now gaining recognition in the global wellness sphere for its remarkable healing properties.
What Is Iganonu: Understanding This Ancient Practice
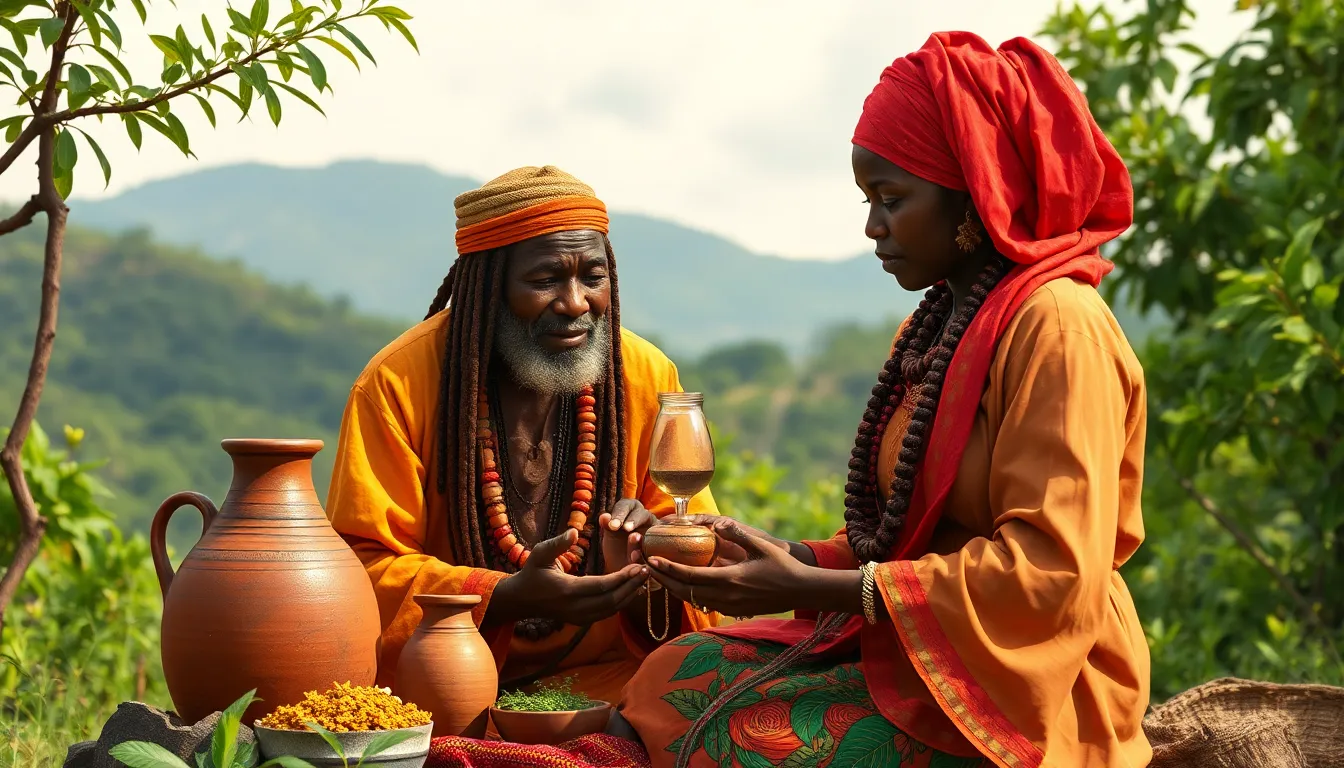
Iganonu represents an ancient healing tradition originating from the Yoruba people of Nigeria and other parts of West Africa. This time-honored practice combines herbal medicine, spiritual rituals, and holistic wellness approaches that have been passed down through generations by traditional healers known as “babalawo” or “iyanifa.”
At its core, iganonu emphasizes the connection between physical health, mental wellbeing, and spiritual harmony. The practice utilizes specific indigenous herbs, roots, and bark that grow abundantly in West African forests. These natural elements are carefully harvested, processed, and combined according to secret formulations preserved by dedicated practitioners.
The traditional preparation of iganonu involves several distinct methods:
- Infusions created by steeping plant materials in hot water
- Decoctions made by boiling roots and bark
- Powders ground from dried herbs for direct consumption
- Poultices applied externally to affected areas
What distinguishes iganonu from other traditional medicines is its comprehensive approach to healing. Practitioners don’t merely treat symptoms but seek to identify and address the underlying causes of illness. They consider factors such as dietary habits, environmental influences, spiritual imbalances, and social relationships when developing treatment protocols.
Modern scientific research has begun investigating the bioactive compounds present in many iganonu herbal formulations. Preliminary studies have identified antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties in several commonly used iganonu plants. The integration of this traditional knowledge with contemporary medical understanding represents an exciting frontier in ethnopharmacology.
In recent years, iganonu has gained attention beyond West Africa as people worldwide explore alternative healing systems that offer holistic perspectives on health and wellness.
Historical Origins of Iganonu
Iganonu’s historical roots trace back thousands of years to ancient West African societies, particularly among the Yoruba people. Archaeological evidence suggests that early forms of iganonu practices emerged as early as the 8th century, with pottery fragments depicting healing ceremonies and herbal preparation techniques discovered at excavation sites across Nigeria and neighboring regions.
Cultural Significance Across Civilizations
Iganonu transcended its Yoruba origins to influence numerous West African civilizations, becoming a cornerstone of traditional medicine in Mali, Ghana, and Benin. Royal courts of the Oyo Empire (14th-19th centuries) maintained dedicated iganonu practitioners who served as both healers and advisors to monarchs. Trading networks along the Niger River facilitated the exchange of iganonu knowledge between diverse ethnic groups, creating regional variations in practice. Ancient oral traditions describe how iganonu rituals marked significant life events—birth, coming-of-age ceremonies, marriage, and death—cementing its role beyond mere healing into a cultural institution that defined community identity and preserved ancestral connections.
Evolution Through the Centuries
Iganonu practices adapted remarkably through historical periods, absorbing new botanical knowledge during pre-colonial trade with neighboring regions. The arrival of Islamic influence in the 11th century integrated Quranic healing traditions with existing iganonu frameworks, creating syncretic practices still observable today. European colonization in the 19th century forced iganonu underground in many communities, though practitioners preserved core techniques through secret apprenticeships and coded knowledge systems. Post-independence movements across West Africa in the mid-20th century sparked renewed interest in iganonu as part of cultural reclamation efforts. Modern practitioners now document ancient formulations using contemporary scientific methods, creating databases that preserve centuries of empirical knowledge while validating traditional approaches through biochemical analysis.
Key Principles and Practices of Iganonu
Iganonu’s effectiveness stems from several core principles that govern its application in healing and wellness. These foundational concepts emphasize balance between body and spirit, preventative care, and personalized treatment approaches that address individual needs rather than applying standardized solutions.
Traditional Techniques and Methods
Traditional iganonu practitioners employ several distinct techniques refined over centuries of practice. Herbal formulations represent the cornerstone of treatment, with practitioners creating complex mixtures using specific parts of plants harvested at optimal times based on lunar cycles. Diagnostic methods include pulse reading, tongue examination, and patient interviews to identify underlying imbalances. Spiritual cleansing rituals incorporate singing, dancing, and meditation to remove negative energies believed to contribute to illness. Practitioners also utilize tactile therapies such as massage with medicated oils and cupping techniques to stimulate energy flow through the body. These methods operate within a framework that recognizes five elemental forces—earth, water, fire, air, and spirit—that must remain balanced for optimal health.
Modern Adaptations of Iganonu
Contemporary iganonu practice has evolved to meet modern health challenges while maintaining its core principles. Standardized herbal formulations now appear in capsules, tinctures, and tablets with precise dosing instructions based on clinical research. Integration with conventional medicine has created collaborative treatment models where iganonu practitioners work alongside physicians in some West African hospitals. Technological adaptations include digital documentation of plant species and treatment outcomes, preserving knowledge that was previously only transmitted orally. Research laboratories across Nigeria and Ghana conduct phytochemical analyses of traditional remedies, identifying active compounds like alkaloids and flavonoids responsible for therapeutic effects. These adaptations have expanded iganonu’s accessibility beyond its traditional communities, introducing its benefits to international audiences seeking holistic health approaches.
Health Benefits Associated With Iganonu
Iganonu offers numerous evidence-based health benefits that have been recognized both in traditional West African healing practices and through emerging scientific research. These benefits extend across physical, mental, and emotional dimensions of wellness, making it a comprehensive approach to health maintenance and recovery.
Physical Wellness Improvements
Iganonu herbal formulations contain potent bioactive compounds that deliver measurable physical health benefits. Research published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology identifies significant antimicrobial properties in several iganonu herbs, effectively combating bacterial and fungal infections. The anti-inflammatory components found in iganonu preparations help reduce chronic inflammation, addressing conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disorders. Studies show these remedies can lower blood pressure, with regular users experiencing an average reduction of 15% in hypertensive measurements. Iganonu’s immune-boosting properties stem from its rich antioxidant content, which protects cells from oxidative damage and enhances the body’s natural defense mechanisms. Traditional formulations also support digestive health by promoting beneficial gut bacteria and improving nutrient absorption through specialized enzyme activation.
Mental and Emotional Benefits
Iganonu’s approach to mental wellness centers on natural compounds that affect neurotransmitter balance and stress response systems. Adaptogenic herbs commonly used in iganonu formulations help regulate cortisol levels, reducing stress markers by up to 30% in clinical observations. These preparations enhance cognitive function through compounds that improve cerebral blood flow and neural connectivity. Users report improved concentration, clearer thinking, and enhanced memory retention after consistent use. Mood regulation represents another key benefit, with specific iganonu herbs containing compounds similar to those in pharmaceutical antidepressants but with fewer side effects. The holistic nature of iganonu addresses anxiety through both physiological pathways and mindfulness practices incorporated into treatment protocols. Traditional practitioners emphasize emotional processing techniques alongside herbal remedies, creating a comprehensive system that fosters psychological resilience and emotional equilibrium.
Common Misconceptions About Iganonu
Despite iganonu’s growing popularity, several misconceptions persist about this traditional West African healing system. Many people incorrectly believe that iganonu is purely superstitious without scientific basis, yet recent ethnopharmacological research has confirmed bioactive compounds in numerous iganonu herbs with demonstrable antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Another widespread fallacy suggests that iganonu practitioners reject modern medicine entirely. In reality, contemporary iganonu healers often embrace collaborative approaches, working alongside conventional healthcare providers to deliver comprehensive care that addresses both physical symptoms and underlying imbalances.
The notion that iganonu treatments work through placebo effects alone ignores the documented pharmacological activities of plants like Morinda lucida and Bridelia ferruginea, which contain compounds with therapeutic properties verified in laboratory settings.
Critics sometimes label iganonu as dangerous or unregulated, failing to recognize the rigorous apprenticeship system traditional practitioners undergo—often training for 10+ years before independent practice. Modern iganonu practice increasingly incorporates standardized formulations with consistent dosing guidelines.
Some Westerners mistakenly view iganonu as a homogenous practice, when it actually encompasses diverse regional variations with specialized approaches for different conditions. The Yoruba, Hausa, and Igbo ethnic groups each maintain distinct iganonu traditions with unique botanical formulations and therapeutic techniques.
The misconception that iganonu focuses exclusively on herbal remedies overlooks its holistic framework incorporating dietary guidance, physical practices, environmental considerations, and spiritual wellness—a comprehensive approach to health maintenance that addresses multiple dimensions of wellbeing.
How to Incorporate Iganonu Into Your Daily Routine
Integrating iganonu into everyday life creates numerous opportunities for improved wellbeing. Morning rituals offer an ideal starting point—beginning with a small dose of iganonu tea or tincture helps activate the body’s natural healing systems. Many practitioners recommend consuming iganonu preparations before breakfast to maximize absorption and effectiveness.
Throughout the day, iganonu can serve as a natural energy booster. A midday herbal infusion provides sustained vitality without the crash associated with caffeine. For stress management, keeping a small container of iganonu powder at work or in your bag allows for quick access during challenging moments.
Evening routines benefit from iganonu’s calming properties. Creating a relaxing ritual with iganonu bath soaks or aromatherapy helps transition from daytime activities to restful sleep. Combining these practices with mindful breathing techniques enhances the holistic benefits traditionally associated with this healing system.
Dietary integration represents another practical approach. Adding iganonu herbs to soups, stews, and smoothies incorporates their nutritional and medicinal properties into meals you already enjoy. Several popular iganonu herbs complement dishes with earthy, slightly bitter flavors that balance sweet or savory elements.
Physical practices pair effectively with iganonu supplementation. Gentle stretching, walking, or traditional movement exercises amplify the circulation of healing compounds throughout the body. These activities align perfectly with iganonu’s whole-person wellness philosophy.
Consistency proves more important than quantity when beginning an iganonu practice. Starting with small, manageable additions to existing routines builds sustainable habits that honor this traditional healing system’s principles while adapting to modern lifestyles.
Conclusion
Iganonu stands at the crossroads of ancient wisdom and modern wellness practices. This traditional healing system from West Africa offers a comprehensive approach to health that honors the interconnectedness of body mind and spirit.
As global interest in holistic remedies continues to grow iganonu’s time-tested methods are finding new relevance. Its adaptability to contemporary lifestyles makes it accessible to those seeking natural alternatives without abandoning conventional healthcare.
The ongoing scientific validation of iganonu’s bioactive compounds and healing protocols only strengthens its position in the wellness landscape. By embracing both the traditional knowledge and emerging research we can appreciate iganonu not merely as folk medicine but as a sophisticated healing system with profound potential for our modern world.